Cause of occurrence and current state of environmental refugees
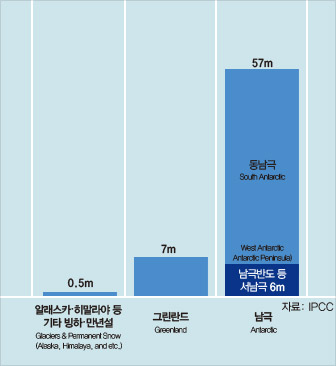
Decrease in Glaciers Due to Global Warming
Glaciers, which is called the Earth’s refrigerator, have been melting down and it accelerates global warming; as global warming melts glaciers, it causes a vicious circle.
Pedersen Glacier
McCarty Glacier - Alaska
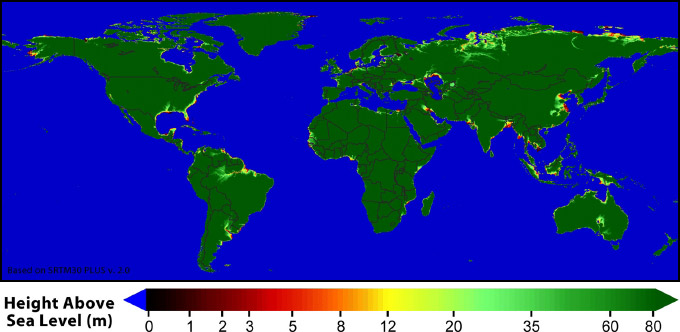
The Effect of Sea-Level Rise
- 1. Loss of Land
- 2. Destruction of Livelihood
- 3. Shortage of Food (Soil salinization makes agriculture impossible.)
- 4. Shortage of Drinking Water (Inflow of seawater salinizes fresh water.)
- 5. Impact of Tsunamis and Storms Will Be Worsened
- 6. Occurrence of Environmental Refugees
- 7. The Accumulative Effects of Sea-Level Rise Can Threaten the Survival of Humankind
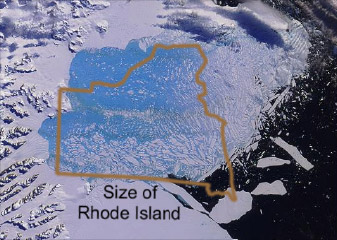
"I was stunned to know that glaciers are melting far faster than expected.
For example, the Larsen B ice shelf that is five times bigger than the city of Seoul completely disintegrated into the ocean over a 35-day period from January 31 to March 7, 2002.”
The UN Secretary-General, Ban Ki-moon (in an interview after visiting the Antarctic in 2007)
Environmental Refugees
1. Definition
It refers to people who are forced to migrate from or flee their home region due to sudden or long-term changes to their local environment which compromise their well being or secure livelihood, such changes are held to include increased droughts, disforestation, starvation due to the rapid population increase, desertification, sea level rise, and disruption of seasonal weather patterns such as monsoons. It includes the terms, such as 'environmental refugee' and 'climate refugee.‘
2. The Status of Environmental Refugees Around the World
As of 2010, there are 42 million climate refugees throughout the world. And it is expected that climate refugees will reach one billion by 2050. (Source- IDMC [Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre], Norwegian Refugee Council, ADB [Asian Development Bank])
3. International policy on environmental refugees
Although they rapidly increase in number, climate refugees are not considered refugees under the international legal definition. There is little aid for climate refugees because they are not considered refugees under the international legal definition, whlie the refugees fleeing political oppression are supported with finance, food and education from governments of international organizations. It is urgent to prepare legal grounds to support climate refugees.
4. The voice from around the world for environmental refugees
Norman Myers - Green College, University of Oxford
“Environmental refugees totalled at least 25 million people, compared with 27 million traditional refugees (people fleeing political oppression, religious persecution and ethnic troubles).”
- New Economics Foundation (NEF), a progressive research institute of the UK
- “Climate disasters such as sea-level rise is being driven by the fossil fuel-intensive lifestyles the West enjoys.”
“Nevertheless, as they cannot gain refugee statues under the international legal definition, it is just their own government that should cope with it.”
- Andrew Simms - NEF’s policy director
- "An alternative to an amended Geneva Convention is a new convention specifically focusing on people whose way of life is being destroyed. The world need to establish an internationally agreed measure of ecological debt.”
- Achim Steinier - The Deputy Secretary-General of the UN and the Executive Director of the UN Environment Programme(UNEP)
- “Indeed there are many island nations who are doomed already now, condemned, to disappear.
Therefore, there is no question that we have to act. And that is just the beginning of the visible impact of climate change.”
- Anote Tong, The President of Kiribati
- “We have whole communities, having to be relocated, villages which have been there over a decade maybe the century and now they have to be relocated, and where they’ve being living for the last few decades is no longer there. It has been eroded.
We may be at the point of no return; our small low lying island will be submerged. It’s an issue of human survival. If the world community, the different countries don’t kick the Carbon habits, there will be other countries next on the line.”
- Paul Tobasi - Government Representative for the Carteret Islands
- “It’s not their wish to go, but because of the situation; it’s forcing them to move.”
- Sheikh Hasina - The Prime Minister of Bangladesh
- “The seawater has permeated the lands around the shore and they became the cursed lands where people cannot live anymore. This is the climate terrorism.”
Environmental refugee by sea level rise
Island nations submerged or vulnerable to sea level rise (around 40 island nations)
- 1. Tuvalu
- “Tuvalu is one of the countries suffering the most extreme environmental stresses in the context of climate change.”
Climate change, sea level rise, saltwater intrusion, and ocean acidification have serious implications for both Tuvalu’s food security and economic development.
Because global efforts to reduce emissions have been grossly inadequate, Tuvalu must prepare for unavoidable climate change impacts.
Tuvalu is concerned about global increases in greenhouse gas emissions and their effect on rising sea levels, which threaten the country's underground water table; in 2000, the government appealed to Australia and New Zealand to take in Tuvaluans if rising sea levels should make evacuation necessary
- 2. Kiribati
- 107,800 residents, about 30 islands around Kiribati are being submerged
- 3. Maldives
- 369,000 residents, 85% of the land will be submerged by the 1m increase of the sea level
- 4. Papua New Guinea
- 5. India
- lohachara - 10,000 residents
Bedford, Cabaskadi, Supalibaga islands around India, 6.000 residents, 6,000 households
50 Sundarbans islands - 2 million residents are threatened
- 6. The United States of the America
- 13 islands in Chesapeake Bay of Maryland
- 7. Bangladesh
- 10 million refugees, 15~20million refugees when the sea level rises 1m
Coudubtia island of Bengal Bay –5percent of area decreased, residents became homeless people
Half area of Bhola island –00,000 residents
- 8. Islands around Saga - 50,000 residents
- 9. Marshall Islands - 60,000 residents
- 10. Tonga - 16,900 residents
- 11. Vanuatu - 212,000 residents, Some of the residents migrated
- 12. Solomon Islands - 66,800 residents
- 13. Cateret Islands of Papua New Guinea - 500 residents stopped crop producing
- 14. Shshmarephin, Alaska, USA - 600 residents, Kabalini, Alaska, USA - 400 residents
- 15. Around 2,000 Islands of Indonesia
- 16. Dubai - 120 residents in need
- 17. Vietnam - 10 million refugees when the sea level rises 1m
- 18. Palau - 30,000 residents
Above this, many island nations which are not uninhabited or not reported are submerging or were submerged already due to climate change.